-
Photophysics and Photochemistry of the UV Filter Kynurenine Covalently Attached to Amino Acids and to a Model Protein
P.S. Sherin, J. Grilj, L.V. Kopylova, V.V. Yanshole, Y.P. Tsentalovich and E. Vauthey
Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 114 (36) (2010), p11909-11919


DOI:10.1021/jp104485k | unige:14788 | Abstract | Article HTML | Article PDF
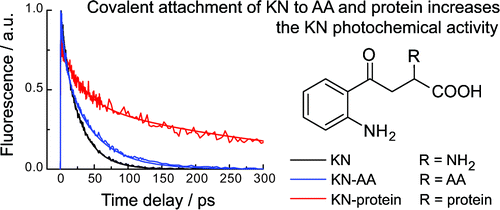
The photophysics and photochemistry of kynurenine (KN) covalently bound to the amino acids lysine, cysteine, and histidine, the antioxidant glutathione, and the protein lysozyme have been studied by optical spectroscopy with femto- and nanosecond time resolution. The fluorescence quantum yield of the adducts of KN to amino acids is approximately 2 times higher than that of the free KN in solution; KN attached to protein exhibits a 7-fold increase in the fluorescence quantum yield. The S1 state dynamics of KN-modified lysozyme reveals a multiphasic decay with a broad dispersion of time constants from 1 ps to 2 ns. An increase of the triplet yield of KN bound to lysozyme is also observed; the triplet state undergoes fast intramolecular decay. The obtained results reveal an increase of the photochemical activity of KN after its covalent attachment to amino acids and proteins, which may contribute to the development of oxidative stress in the human lensessthe main causative factor for the cataract onset.